Research project Experiments with beams of cold stored ions in DESIREE
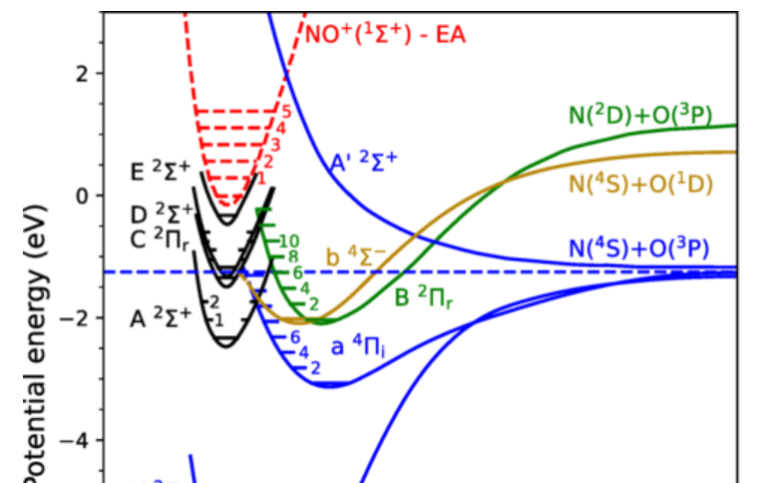
Mutual Neutralization (MN) is studied at the DESIREE ion-beam storage ring. In MN, an electron is transferred from a negative to a positive ion forming two neutral particles. This fundamental process is important in many natural environment.

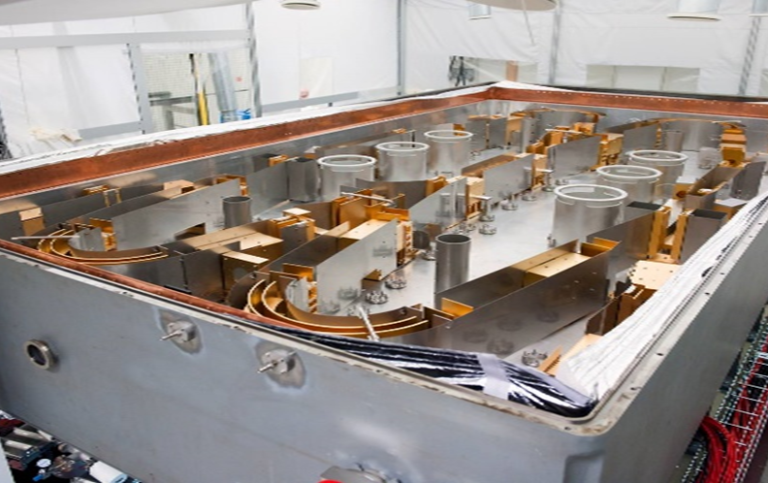
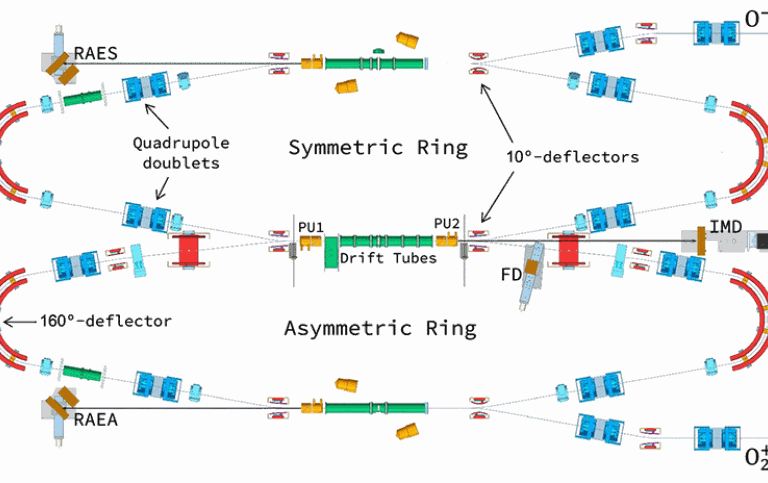
Mutual neutralization is the process where an electron is transferred from an anion to a cation forming two neutral atoms or molecules. This project's primary purpose is to measure mutual neutralization with control of internal degrees of freedom (i.e. the quantum states occupied forboth ions) and their relative motion. In the cryogenic electrostatic double ion-storage ring, DESIREE, beams can now be stored for long times in
cryogenic environments allowing the ions to cool down internally.
We use these unique conditions to investigate this process for a wide range of atomic and small molecular ions of fundamental interest. We investigate mutual neutralization processes of relevance in the interstellar medium and between H- and positive metal ions, which is of significance for the understanding of stellar atmospheres and stellar metal abundances.
Project members
Project managers
Henning Schmidt
Professor

Members
Alice Frederike Schmidt-May
PhD student
Publications
Experiments with beams of cold stored ions in DESIREE