Research project Supersymmetric Top Quark Partners at the LHC
A supersymmetric extension of the standard model can solve the fine-tuning problem of the Higgs mass and explain dark matter. In this project we search for the supersymmetric partner of the top quark with data from the ATLAS experiment at CERN.
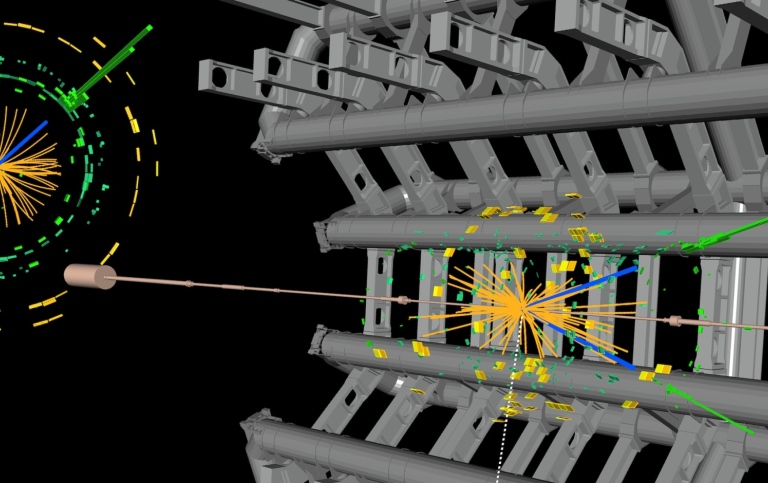
The main objective of the project is to search for new particles which presence can solve the Higgs fine-tuning problem. In the Standard Model of particle physics, the top quark gives rise to a large quantum correction to the Higgs boson mass which has to be counter-balanced by a fine-tuned free parameter in order to arrive at the measured Higgs boson mass. The correction from the top quark can be controlled by introducing a supersymmetric top-quark partner (stop) with a mass below approximately 1.5 TeV, i.e. within reach by the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN. As a supersymmetric extension of the current theory can also provide a dark matter candidate and allows for a unification of the electroweak and the strong forces of nature, the discovery of a stop would have implications far beyond solving the Higgs fine-tuning problem.
Project description
In this project, we conduct searches for the stop with data from the ATLAS experiment at CERN. We cover a broad range of scenarios which are still viable given the results of already existing searches. At the end of the project, the result will either be a discovery or a set of limits on the masses of supersymmetric particles. The project also involves the development of new search strategies and techniques, which are expected to be of lasting benefit and use to the field.
Project members
Project managers
Members
Ellen Maria Riefel
PhD student

Antonia Strübig
Postdoc